KEY POINTS
- Education reform is essential to address Ghana’s skill mismatch crisis.
- SME support can boost job creation and stabilize the economy.
- Entrepreneurship drives innovation, expanding job options for Ghanaian youth.
Ghana faces a growing youth unemployment crisis that threatens the nation’s economic future. With a significant portion of its population under 25, the country’s young workforce holds the potential to drive economic growth.
Yet, economic volatility, skill mismatches, and limited opportunities continue to hinder many young Ghanaians from finding employment. Tackling these issues is critical to strengthening Ghana’s development path and empowering its youth.
Factors contributing to youth unemployment in Ghana
A significant factor contributing to youth unemployment in Ghana is the discord between the school system and the requirements of the job market. Many young Ghanaians graduate with skills that do not correspond with labour market requirements, leading to elevated rates of underemployment and unemployment. Africa News reports that a skills mismatch adversely affects graduates in disciplines with few career opportunities, while industries such as technology and engineering experience skill shortages, resulting in young individuals being either underqualified or overqualified for the positions available.
The economic volatility in Ghana further aggravates youth unemployment. The economy is significantly dependent on agriculture, mining, and energy exports, which are susceptible to global price volatility. According to Al Jazeera, Ghana’s economy is adversely affected by escalating inflation and currency depreciation, which undermine employment prospects and restrict economic resilience. Small and medium-sized firms (SMEs), which have the potential to generate essential employment, frequently encounter obstacles such as elevated taxation, inadequate infrastructure, and insufficient cash for expansion.
Cultural norms and little entrepreneurial assistance exacerbate youth unemployment. A significant number of young individuals lack access to mentorship and essential resources for initiating their enterprises. Despite the recent rise of Ghana’s entrepreneurship industry, resources for young entrepreneurs continue to be scarce. Furthermore, numerous young Ghanaians encounter societal pressures that prioritize conventional job trajectories over entrepreneurship, impeding innovation and growth potential.
Strategies for addressing Youth unemployment in Ghana
Ghana requires a multifaceted strategy to tackle young unemployment. The government and the commercial sector must collaborate to synchronize educational programs with labour market requirements. Collaborations between universities and employers can guarantee that students receive training in high-demand sectors, including technology, engineering, and healthcare. Vocational and technical education must be prioritized to furnish young individuals with practical skills directly relevant to existing employment opportunities.
Facilitating entrepreneurship is an essential tactic. The government can assist young entrepreneurs by providing grants, low-interest loans, and business training. Initiatives that foster startup development in burgeoning industries, such as renewable energy and digital technology, will broaden career prospects and enable youth to generate their employment chances.
Enhancing the business environment for SMEs is crucial. Streamlining tax frameworks, providing financial incentives, and enhancing infrastructure will facilitate the expansion of SMEs and the recruitment of additional personnel. Promoting rural economic growth, especially via infrastructure expenditures, can alleviate urban job-seeking pressures by generating employment opportunities locally.


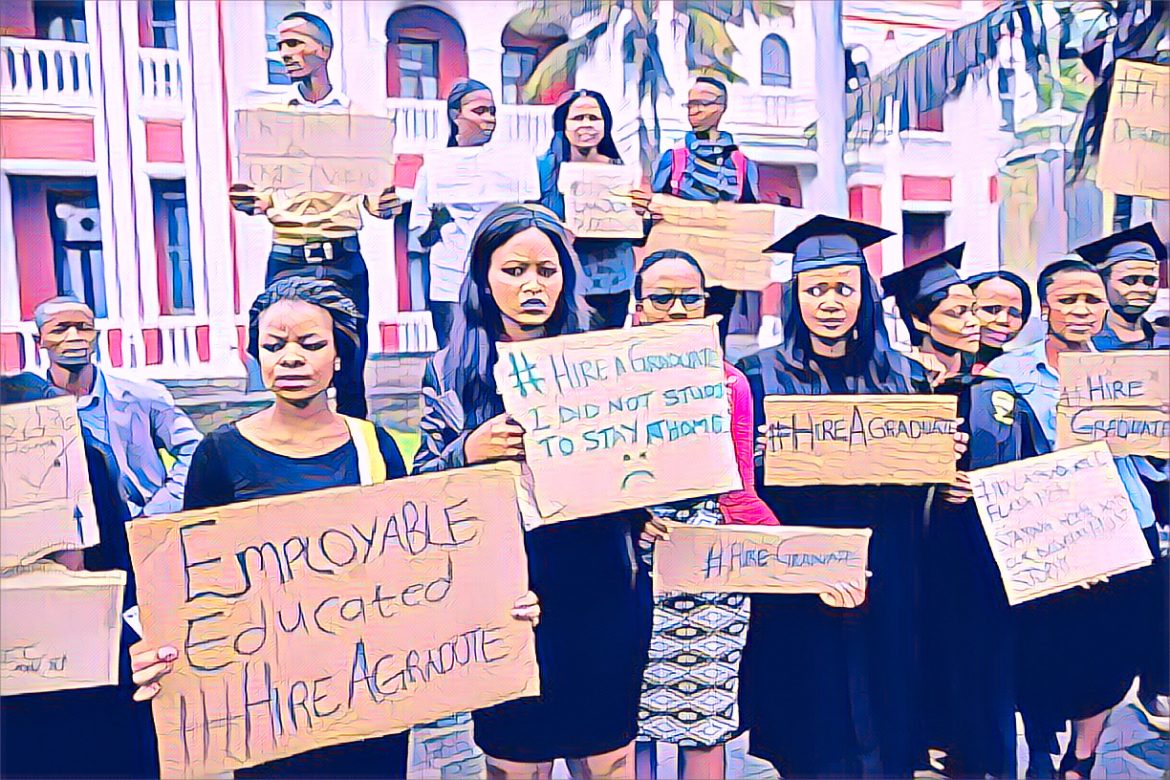


8 comments
I have been surfing online more than 3 hours today, yet I never found any interesting
article like yours. It is pretty worth enough
for me. In my opinion, if all site owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the web will be much more useful than ever before.
Very good post! We are linking to this great content on our website.
Keep up the good writing.
Das Hotel verfügt über ein außergewöhnlich buntes
Freizeitangebot, welches jedem Urlauber unvergessliche Momente bereiten wird.
Das New York New York Hotel & Casino in Las Vegas bietet seinen Gästen eine einzigartige
Erfahrung, die das pulsierende Leben der Metropole New York
perfekt widerspiegelt. Die Players Suite bietet Platz für bis zu
5 Personen und eignet sich ideal für eine Gruppe von Freunden. Das New
York-New York Hotel & Casino bietet Ihnen einen komfortablen Aufenthalt nach einem Abend
in Las Vegas. Das Hotel bietet M Life Rewards für Ermäßigungen auf
das Angebot im gesamten Hotel, einschließlich Suiten, Unterhaltung und Speisen. Das Casino bietet 7.804 m2 Platz für ein spannendes Spieleerlebnis.
Baisley Pond Park ist 850 Meter entfernt. Das im Stadtteil Queens gelegene Rodeway Inn Near JFK Airport New
York bietet einen Gepäckraum, einen Safe und einen Warenautomaten. Thurston Basin liegt in unmittelbarer Nähe
zum Hotel. Das Hotel liegt in erstklassiger Lage im Bezirk Queens.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/rant-casino-freispiele-alles-was-sie-wissen-mussen/
I’ve been using Neospin to play pokies ever since it was released in 2022 – it’s
a very popular online casino here in Australia. The $500 VIP program entry and the missing table games section are just minor drawbacks in an otherwise
top Australian online casino. After my pokies session, I tried a couple of unusual live casino games
like Monopoly and Andah Bahar (just to take a break from the usual blackjack and roulette), and
the experience was overall great. If a casino looks generic, it usually
IS generic, and I’ve got nothing against mediocrity – but this
is a list of the best online casinos in Australia after all.
This means that online casinos cannot operate legally in Australia.
We are a whole team working together to bring you updated
picks of the best Australian online casinos based on their safety, payout history, software partners, and more.
There’s also a whole section dedicated to table games, with all the classics like blackjack,
roulette, baccarat, and online poker. Regular players are
kept engaged with weekly promotions, including up to 20% daily cashback and
a 66% weekend reload bonus of up to A$1,000. Our
recommended online Australian casinos fall into this
category. While online gambling is hugely popular in Australia, the rules around online gambling sites can be confusing.
Whether I’m reviewing a pokie, analysing a bonus, or
auditing a casino’s licensing, I approach every piece with honesty, clarity, and a commitment to responsible gambling.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/review-of-billion-dollar-gran-slot/
You can log in at any time from anywhere in Australia to
enjoy your favorite casino games. Log in now to access your account and enjoy premium gaming entertainment.
Visit the promotions section to view and activate available King Billy
bonus offers for Australian players. Simply log in to your King Billy account and start playing instantly from your mobile device anywhere in Australia.
The responsive design automatically adapts to your device for seamless King Billy login and
gameplay. Welcome to the official King Billy Casino login gateway—your fast, private,
and compliant path to the royal gaming experience.
Whether you prefer credit cards, e-wallets, or digital currencies, King Billy’s payment infrastructure delivers seamless financial management with processing times optimized for Australian players.
King Billy Casino understands that modern Australian players value
flexibility and convenience. After registration, accessing your account is simple.
Australian players conduct all transactions in AUD without conversion fees or exchange rate fluctuations
affecting their bankroll. King Billy Casino
specifically addresses the needs and preferences of the Australian gaming
market through localized features and services. Roulette options include European,
American, and Lightning variants, each offering unique gameplay mechanics
and payout structures. These instant-win options appeal to players seeking
quick results and transparent outcomes based on provably fair
algorithms.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/news-update-online-gambling/
I am not sure where you are getting your info, but great topic.
I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more.
Thanks for great information I was looking for
this information for my mission.
online casino roulette paypal
References:
http://my.calientalomedia.com/lukeqca108
casino online uk paypal
References:
jobsercher.com