KEY POINTS
- MTN Mobile Money leads Ghana’s mobile financial revolution, providing innovative services and enhancing access for millions.
- Cashless payment systems drive economic growth and financial inclusion through digital wallets, card payments, and online banking.
- Regulatory oversight and security measures are critical as Ghana expands mobile money and cashless transactions.
Over the past decade, Ghana has emerged as a leader in Africa’s digital financial revolution, driven by the rapid growth of mobile money and cashless payment systems (CGAP, 2018).
The advent of mobile money services has transformed how Ghanaians conduct financial transactions, significantly improving financial inclusion and catalyzing economic growth (CELL PRESS).
With more than 30 million mobile money subscribers and transactions valued at over GHS 200 billion annually, mobile money has become a cornerstone of Ghana’s financial ecosystem.
Cashless payment systems, including mobile payments, online banking, card payments, and digital wallets, are steadily gaining traction.
The adoption of these systems has been accelerated by advancements in technology, growing internet penetration, and the increasing availability of affordable smartphones.
Let’s explore the rise of mobile money and cashless payments in Ghana, examining the key players, opportunities, challenges, and the future outlook for this transformative sector.
- MTN mobile money
MTN Mobile Money is the dominant player in Ghana’s mobile money market, boasting the largest share of subscribers and transaction volumes.

Launched in 2009, MTN Mobile Money has revolutionized financial transactions by offering services such as peer-to-peer transfers, bill payments, savings accounts, and microloans. Its extensive agent network, covering both urban and rural areas, ensures accessibility for all.
MTN’s innovative platforms, such as MoMo Pay, have further enhanced its appeal. Businesses use MoMo Pay for seamless payment processing, reducing reliance on cash transactions.
MTN’s partnerships with banks and fintechs have also facilitated the integration of mobile money with traditional banking services, creating a comprehensive financial ecosystem. This integration underscores MTN’s pivotal role in driving financial inclusion and economic growth in Ghana.
2. Vodafone cash
Vodafone Cash is a notable competitor in the mobile money space, known for its user-friendly services and commitment to innovation. The platform’s unique features, such as free transfers between Vodafone Cash users and discounted transaction fees, have attracted a growing customer base.
Vodafone Cash has also introduced merchant services tailored for small businesses, enabling seamless payments and fostering economic participation.
3. Tigo cash and AirtelTigo money
Tigo Cash, now part of AirtelTigo Money following the 2017 merger, has focused on financial inclusion, especially for the unbanked population. Its simplified registration process and localized services cater to rural and underserved communities. AirtelTigo Money continues to expand its offerings, providing innovative services like instant microloans and international remittances, further strengthening its position in the market.
Cashless payment systems in Ghana
1. Online banking
Online banking has witnessed significant growth in Ghana, with banks such as Ecobank and Standard Chartered leading the charge.
These institutions offer digital platforms that allow customers to perform a wide range of transactions, from fund transfers to bill payments, without visiting a branch. Mobile apps with user-friendly interfaces and robust security features have made banking accessible and convenient for Ghanaians.
2. Card payments
Card payments, including debit and credit cards, are becoming increasingly popular in Ghana. Financial institutions, in partnership with companies like Visa and Mastercard, are driving this growth.
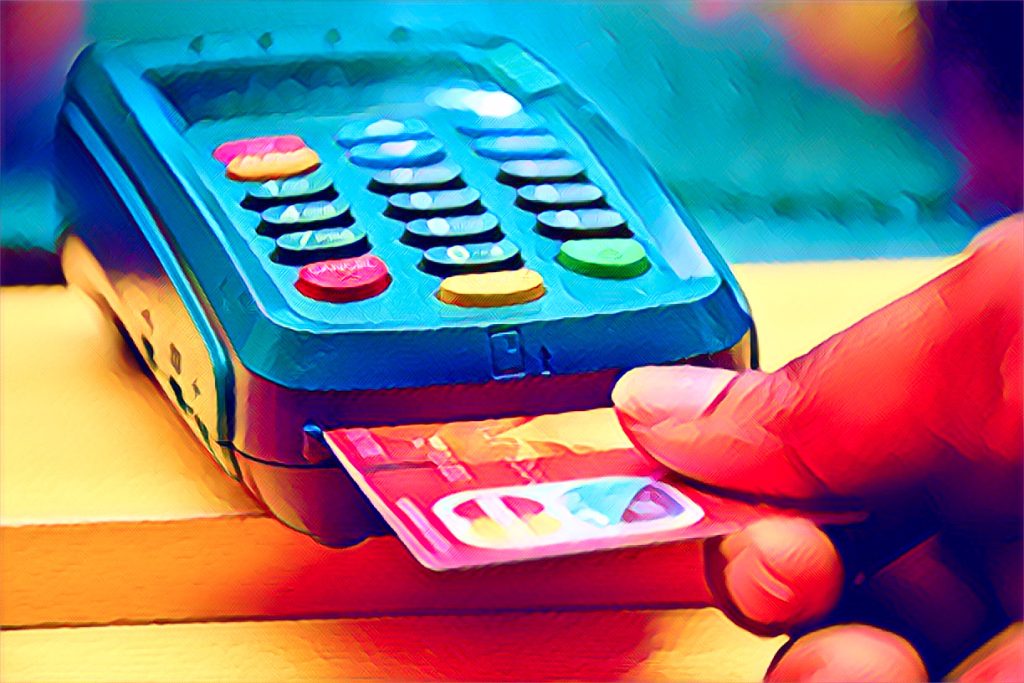

Point-of-sale (POS) terminals are now a common sight in retail outlets, restaurants, and service stations, signaling a shift toward cashless transactions.
3. Mobile payments and digital wallets
Beyond traditional mobile money, digital wallets like PayPal and Mastercard’s QR code payment system are gaining traction. These platforms provide an added convenience layer, enabling users to shop online, pay bills, and transfer funds securely. The government’s focus on digitalization, supported by initiatives like the Ghana Interbank Payment and Settlement Systems (GhIPSS), has further bolstered the adoption of mobile payments and digital wallets.
1. Opportunities
Mobile money and cashless payment systems have created unparalleled opportunities for financial inclusion. Approximately 70 percent of Ghanaians now have access to formal financial services, up from less than 40 percent a decade ago.
The widespread adoption of these systems has unlocked new avenues for entrepreneurship, enabling small businesses to thrive in a digital economy. Moreover, the potential for economic growth is immense, as digital payments contribute an estimated 10 percent to Ghana’s GDP.
2. Challenges
However, the sector faces challenges, including security concerns such as fraud and cyberattacks. Strengthening cybersecurity measures and building public trust remain critical.
Additionally, a robust regulatory framework is essential to protect consumers and ensure the sustainability of these systems. Addressing infrastructure gaps, particularly in rural areas, is also necessary to achieve nationwide penetration.
1. MTN mobile money’s success story
MTN’s ability to combine innovation with an extensive agent network has made it a game-changer in Ghana’s financial landscape.
For instance, the introduction of QR code payments during the COVID-19 pandemic enabled contactless transactions, enhancing safety and convenience.
2. Vodafone cash’s merchant platform
Vodafone Cash’s merchant services have empowered small businesses by offering cost-effective payment solutions. A bakery in Accra, for example, reported a 30 percent increase in sales after adopting Vodafone Cash for customer transactions.
3. Tigo Cash’s financial inclusion initiatives
Tigo Cash’s localized approach has brought financial services to remote communities, enabling farmers to receive payments for their produce instantly and securely.
Ghana’s rise as a leader in mobile money and cashless payment systems is a testament to the transformative power of technology. These systems have revolutionized financial inclusion, driven economic growth, and redefined how Ghanaians engage with financial services.
Innovation, enhanced security measures, and strong regulatory oversight will be crucial to sustaining this momentum. With continued efforts, mobile money and cashless payments have the potential to reshape Ghana’s financial future, ensuring broader economic participation and prosperity for all.





12 comments
Melden Sie sich einfach über Ihren Browser an und das Design passt sich jedem Bildschirm an, auf
dem Sie sich befinden. Erfrischend ist, dass es im Zet Casino online Versionen sowohl für Anfänger als auch für erfahrene Spieler gibt.
Baccarat bietet eine ruhigere Eleganz, während Poker den Wettkampfjuckreiz kratzt,
bei dem sich Geduld auszahlen kann. Sie sind einfach, schnell und tragen immer
diese “nur noch ein Versuch” Energie in sich. Spielautomaten sind der Herzschlag jedes Casinos, und auf der Spielplattform ZetCasino springt dieser Herzschlag nie.
An manchen Tagen möchten Sie einfach gedankenlos ein paar
Walzen drehen und diesem Ansturm nachjagen,
wenn sich die Symbole aufstellen.
Um auf alle Funktionen der Website zuzugreifen, genügt es,
eine einfache Registrierung durchzuführen. Darüber hinaus finden Spieler hier ein ausgezeichnetes Bonusprogramm, nicht nur für Casinospiele, sondern auch für Sportwetten. ZetCasino ist ein zuverlässiges Online-Casino für Spieler
aus Deutschland, das über eine Lizenz verfügt und bequeme Zahlungsmethoden, einschließlich Kryptowährungstoken, anbietet.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/umfassende-betrachtung-des-vulkan-vegas-cashback-programms/
Sie können beim Spiel um Echtgeld aber strategisch
vorgehen und optimale Bedingungen schaffen.
Der Gewinn an einem herkömmlichen Spielautomaten, zum Beispiel mit sechs Walzen und drei Reihen, ist begrenzt.
Außerdem haben Sie eine größere Auswahl an Online Spielautomaten mit einer oft auch besseren Auszahlungsquote.
Gewinne können entweder per Kartenrisikospiel oder Gewinnleiter erhöht werden.
Du musst kein Spielkonto eröffnen, um unsere Premium-Slots zu spielen –
aber dann verpasst du unsere fantastischen zusätzlichen Boni!
Von modernen Online-Slots mit Minispielen, Bonus- und Gamble-Features bis hin zu
klassischen, nostalgischen Slots – alles im coolen Look,
um deinen täglichen Weg zur Arbeit zu versüßen! Von klassischen Tischspielen über aufregende Slot Casino Spiele bis hin zu innovativen Live-Casino-Erfahrungen, gibt
es etwas für jeden Geschmack und jedes Interesse.
Diese Spiele sind ein wesentlicher Bestandteil des Angebots
in einem best online casino. Spieler können die Spannung eines realen Casinos erleben, während sie bequem von zu Hause aus spielen.
Ab ins Mittelalter zur Zeit der Ritter heißt es bei Knightslots.
Darüber hinaus stechen 111 Freispiele mit in See.
Immerhin erhältst du zusätzlich 200 Freispiele. Bis zu 100 € und 100 Freispiele für ausgewählte Slots gehören zum
Willkommenspaket. Dazu gehören zum Beispiel mit Book of Ra und Book
of Dead zwei der bekanntesten Slots mit ägyptischem
Thema. 150 Freispiele sorgen im Rahmen dieses Angebots
noch einmal für einen Paukenschlag.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/verde-casino-auszahlungen-schnell-sicher-einfach/
If you don’t meet the wagering requirements before the expiry date, you
can lose any bonus funds and winnings. For example,
a $100 bonus with a 30x wagering requirement means you
need to wager $3,000 before cashing out. These can quietly deliver more value
than the headline welcome deals. These could include
deposit limits or time checks, for example.
We find sites with familiar and secure payment methods, so you don’t have to.
If a casino doesn’t meet our high standards, it won’t make it to our recommendations — no exceptions.
Casino.org is dedicated to promoting safe and responsible
gambling. Keep gambling fun with our help.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/free-casino-poker-sites-which-one-is-the-very-best/
All the games you can find on our featured websites come
with exceptional gameplay. Each pokie has its own theme, reward system, and
bonus games, so trying out several of them can be really fun, as you will always be in for something different.
Whichever the case, you should know that each website we promote has a large selection of all types of casino games, from frequently played blackjack to
less popular keno.
CasinoNic collaborates with top-tier providers
like Microgaming and NetEnt, delivering a diverse selection of
high-quality games. Queenspins is known for its highly intuitive user interface, allowing players to navigate through various games and
features effortlessly. Dundeeslots further elevates the gaming
experience with attractive promotional deals, including bonuses and free spins.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/casino-winning-odds-best-and-worst-games-chances-to-win/
There’s a daily withdrawal limit, but it’s generous enough for most players
— high rollers in the VIP tiers can unlock more.
Whether it’s pokies, blackjack, or crash games,
the experience feels built for touch from the start.
Rocketplay also features crypto-friendly crash games, instant win scratch cards, and virtual sports
betting. Rocketplay brings together thousands of games from over 50 top-tier studios.
The rocket play no deposit bonus is a perfect starting point.
It’s not bulletproof — no online casino is — but it’s safer than most of what’s out there.
We operate in compliance with all relevant regulations and hold the necessary licenses
to provide online gaming services to Australian residents.
New accounts receive our generous welcome package instantly, allowing you to start playing with
bonus funds right away. Our streamlined registration process takes less
than 2 minutes, getting you from download to gameplay
with minimal delay. It has been specially optimized for smartphones with
various performance levels to guarantee a smooth gaming experience without interruptions.
Complete the verification process to enjoy uninterrupted gaming and fast transactions.
Players can access RocketPlay Casino on desktops and
mobile devices without any issues. The casino supports multiple payment methods, including credit cards, e-wallets, and cryptocurrencies.
Always read the terms and conditions before claiming any bonus.
Click the ‘Sign Up’ button, fill in your details, verify your email address, and you’re
ready to start playing. Experience the thrill of RocketPlay with extra playing power!
References:
https://blackcoin.co/wild-casino-review-safety-games-more/
There is priority parking located on level 1M, available exclusively to Gold, Platinum
and Diamond Members of The Star Club. Use The Star App to track your progress
towards free parking! Alternatively, the rates for a casual visit are listed below,
along with other suggested parking options around Broadbeach.
THEATRELift access is available on the “Stalls” level, which
transport guests down to row – NN. At the time of booking, please inform
our staff of any special requirements. HOTEL ROOMSPlease contact
Reservations for information about our hotel rooms and apartments that cater to special needs.
RESTROOMSAll restrooms in The Star offer easy access to toilet facilities for those with
special needs and disabilities. CAR PARKINGDisabled parking bays are conveniently located close to the car park entrance lobbies.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/australian-online-gambling-a-comprehensive-guide/
online blackjack paypal
References:
jobrails.co.uk
online casino paypal
References:
https://divyangrojgar.com/employer/best-paypal-online-casinos-real-money-deposits-withdrawals-al-com
paypal casinos for usa players
References:
https://www.thewaitersacademy.com/members/delphiasain446/activity/386714/
paypal casino
References:
http://best114.net/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=21
australian online casinos that accept paypal
References:
https://adm.astonishkorea.com/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=3780
casino avec paypal
References:
https://www.89u89.com/index.php?page=user&action=pub_profile&id=387090&item_type=active&per_page=16